一、什么是框架?
- 可以完成一部分功能的半成品项目
二、学习框架的要求
- 配置文件 - 关系、规范
- 流程
- 深入:框架原理、源码
JavaEE三层架构
webservicedao
三、5种框架
3.1 SSH
SpringStrust2Hibernate
3.2 SSM
SpringSpringMVCMyBatis
3.3 无框架与有框架
前后端分离:
Servlet被Strust2或SpringMVC取代JDBC、DBUtils被Hibernate或MyBatis取代Spring连接三层
四、Hibernate
Hibernate框架:ORM框架。- 1级-
JDBC(全自己写) - 2级-
DBUtils/MyBatis(自己写sql,但不用自己封装对象)、 - 4级-
hibernate(全自动,开发成本高) - Object Relationship Mapping:对象关系映射:类、表之间的关系
- 一张表对应一个实体类
五、案例 — CRM
- CRM:Customer Relationship Management
5.1 搭建Hibernate框架的步骤
5.1.1 导jar包
hibernate/lib/required- 数据库驱动包
5.1.2 准备数据库和实体类
Customer
5.1.3 Eclipse本地导入约束的步骤(或联网)
XML CATALOG
- 进入Window -> Preference -> 搜索 XML Catalog -> 点击 add -> Location分别定位到
hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd和hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd
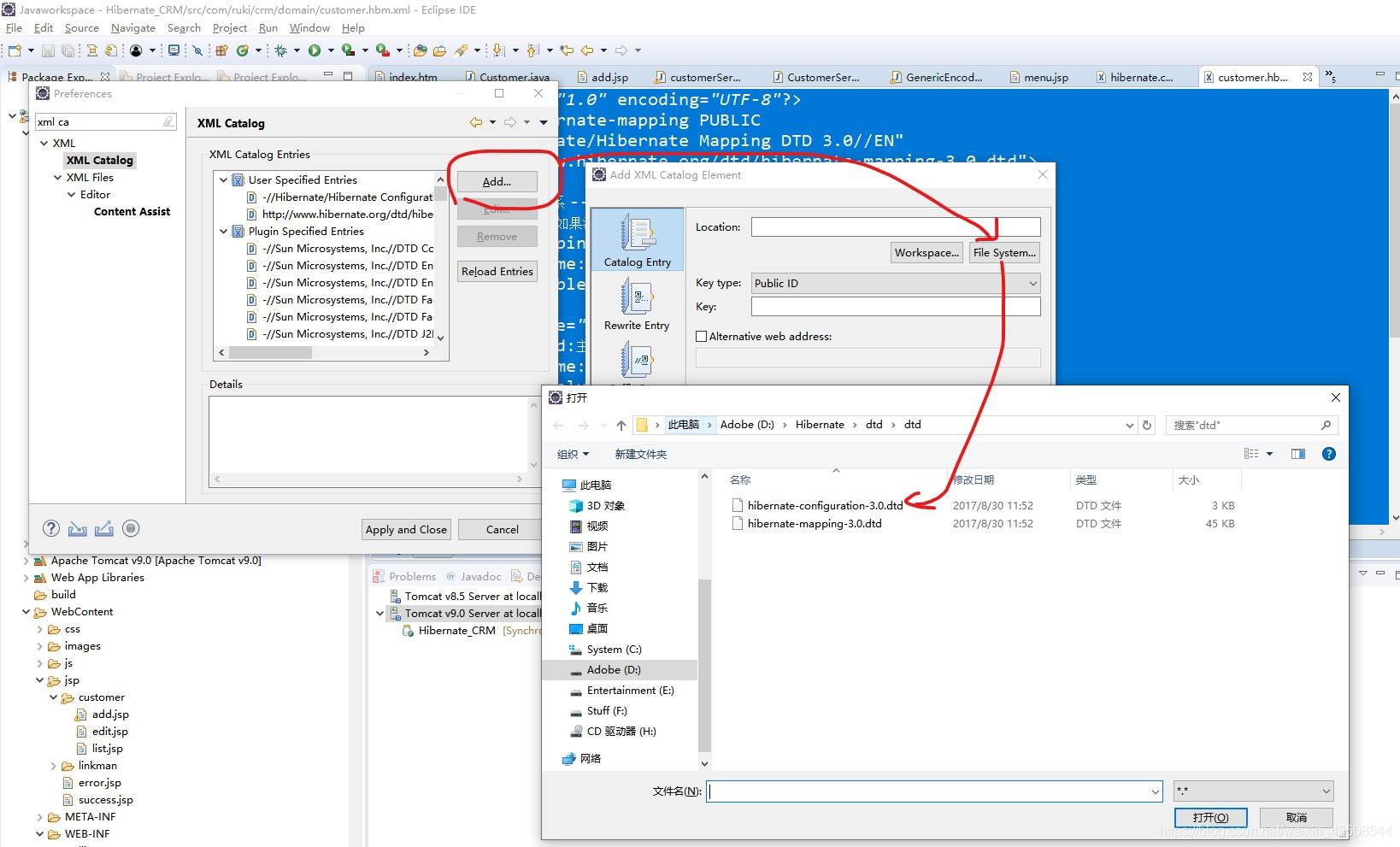
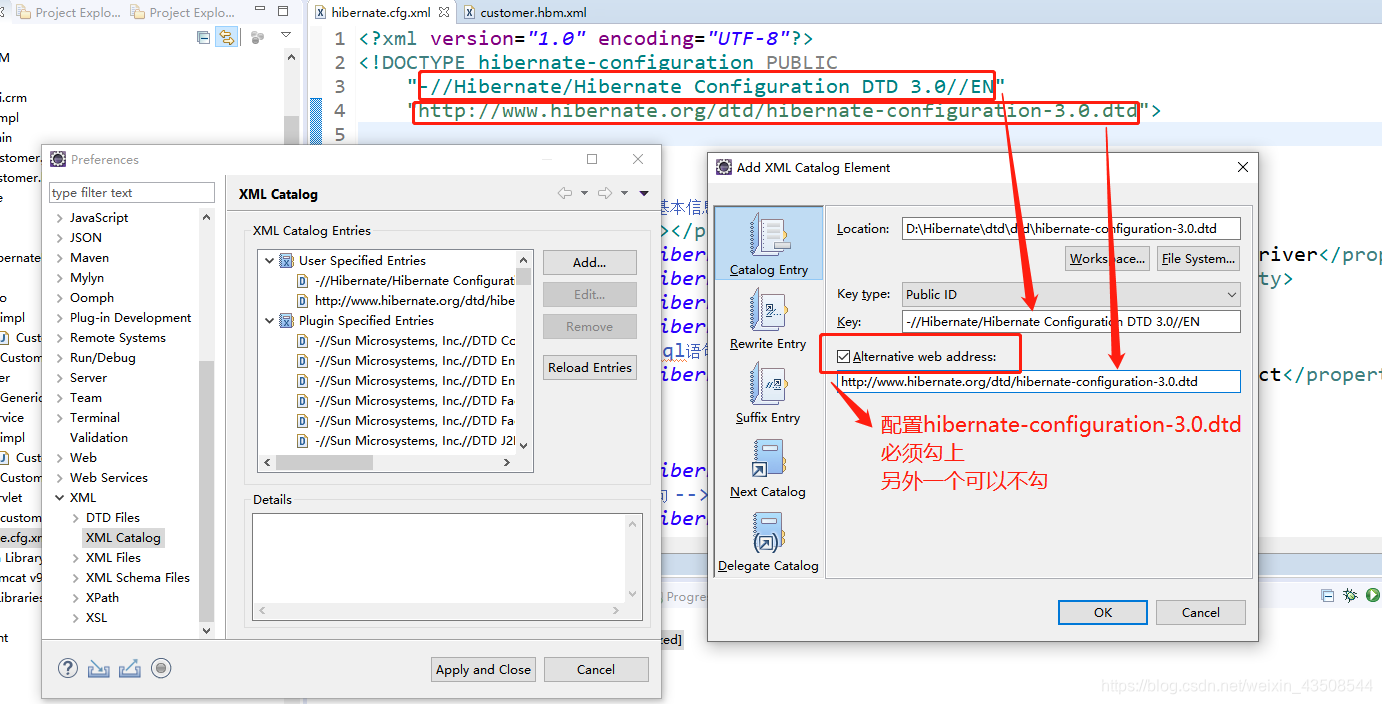
- 进入Window -> Preference -> 搜索 XML Catalog -> 点击 add -> Location分别定位到
- 复制Doctype
配置文件
2种
Hibernate主配置文件:src/hibernate.cfg.xml- 连接数据库:
url(ip port),username,password, 驱动名 配置文件键值对:
解压文件/project/etc/hibernate.property5个必填,3个选填
<font color="red">必填*5</font>:
dialectdriverurlusernamepassword
<font color="red">选填*3</font>:
show_sqlformat_sqlhbm2ddl
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Configuration DTD 3.0//EN" "http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd"> <hibernate-configuration> <session-factory> <!-- 必填 ,连接数据库的基本信息--> <property name=""></property> <property name="hibernate.connection.driver_class">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</property> <property name="hibernate.connection.url">jdbc:mysql:///ssh</property> <property name="hibernate.connection.username">root</property> <property name="hibernate.connection.password">root</property> <!-- 数据库方言,形成的sql语句规范 --> <property name="hibernate.dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect</property> <!-- 选填 --> <!-- 展示sql语句 --> <property name="hibernate.show_sql">true</property> <!-- 格式化展示的sql语句 --> <property name="hibernate.format_sql">true</property> <!-- ## auto schema export 自动导出表结构 #hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto create-drop - 先删(如果存在)每次操作都是创建新表,操作完再删除表(测试用) #hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto create - 先删(如果存在),每次执行都是创建新表(原表被删除) - 以上两种选项,不建议使用 #hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto update - 如果表不存在,创建表;如果存在,在已有的表中操作; - 如果表结构改变,同时会更新表结构 - 建议使用 #hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto validate - 只在表存在,且表结构正确时可用 --> <property name="hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto">update</property> <!-- 引入映射文件,使用相对路径,加载元数据 customer.hbm.xml resource:从类路径开始 --> <mapping resource="com/ruki/crm/domain/customer.hbm.xml"/> </session-factory> </hibernate-configuration>- 连接数据库:
2. 对象关系映射配置文件:`hibernate-mapping.hbm`
- ORM元数据
- 位置随意,名字推荐:xx.hbm.xml,如:`Customer.hbm.xml`
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC
"-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd">
<!-- 表和实体类的关系 -->
<!-- packages:如果添加包,那么其中的所有类型可以写简单类名 -->
<hibernate-mapping package="com.ruki.crm.domain">
<!-- name:实体类的类名
table:实体类对应的表名
-->
<class name="Customer" table="cst_customer">
<!-- id:主键(不可少),由hibernate维护的表,必须存在主键
name:主键对应的属性名
[column]:主键对应的字段名,当字段和属性一致时,可省略
[type]:类型,字段类型,可以填3中
java类型:java.lang.Long
数据库类型:bigint
hibernate类型:long/string/int
不填自动识别
[length]:字段允许的最大长度
不填,类型允许的最大长度
-->
<id name="cust_id" column="cust_id">
<!-- generator:主键生成策略 -->
<generator class="native"></generator>
</id>
<!-- property:除了主键意外的其他普通属性/字段 -->
<property name="cust_name" column="cust_name"></property>
<property name="cust_source" column="cust_source"></property>
<property name="cust_industry" column="cust_industry"></property>
<property name="cust_level" column="cust_level"></property>
<property name="cust_linkman" column="cust_linkman"></property>
<property name="cust_phone" column="cust_phone"></property>
<property name="cust_mobile" column="cust_mobile"></property>
</class>
</hibernate-mapping>5.1.4 使用
- 加载配置文件
!!!默认加载主配置文件(hibernate.cfg.xml),因此元数据的加载,必须放在主配置文件中
<!-- 加载元数据 customer.hbm.xml -->
<mapping resource="beans/customer.hbm.xml"/>- 通过配置,获得
session-factory - 获得
Session对象,取代Connection - 开启事务
Session操作数据库 增删查改- 增:
save - 删:
delete - 改:
update 查:
get/load- 查询:单独讲,
Hibernate提供了3种查询方式,Criteria
- 查询:单独讲,
- 增:
- 关闭事务(
commit、rollback)) 关闭资源
package test; import org.hibernate.Session; import org.hibernate.SessionFactory; import org.hibernate.Transaction; import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration; import org.junit.Test; import beans.Customer; import utils.HibernateUtils; public class HBNTest { @Test public void test01() { // 1. 加载配置文件 Configuration config = new Configuration().configure(); // 2. 通过配置,获得session-factory SessionFactory factory = config.buildSessionFactory(); // 3. 获得Session对象,取代Connection Session session = factory.openSession(); // 4. 开启事务 Transaction Transaction ts = session.beginTransaction(); // 5. Session操作数据库 增删查改 //5.1 根据id查询Customer对象 /*Customer customer = session.get(Customer.class, 1l);//id是1,1是传入的参数 System.out.println(customer);*/ Customer c = new Customer(); c.setCust_name("腾讯"); c.setCust_linkman("马化腾"); session.save(c); // 6. 关闭事务(commit\rollback)) ts.commit(); // 7. 关闭资源 session.close(); factory.close(); } @Test public void test02() { Session session = HibernateUtils.openSession(); /*//单纯获得事务 Transaction ts = session.getTransaction(); //事务开启 ts.begin();*/ System.out.println(session); // Transaction ts = session.beginTransaction(); } }
package test;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.Transaction;
import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration;
import org.junit.Test;
import beans.Customer;
import utils.HibernateUtils;
public class HBNTest2 {
/**
* 1. 查询
*/
@Test
public void test01() {
Session session = HibernateUtils.openSession();
Transaction ts = session.beginTransaction();
Customer customer = session.get(Customer.class, 1l);
System.out.println(customer);
ts.commit();
session.close();
}
/**
* 2. 增加
*/
@Test
public void test02() {
Session session = HibernateUtils.openSession();
Transaction ts = session.beginTransaction();
Customer c = new Customer();
c.setCust_name("腾讯");
c.setCust_mobile("123456");
session.save(c);
ts.commit();
session.close();
}
/**
* 3. 修改
*/
@Test
public void test03() {
Session session = HibernateUtils.openSession();
Transaction ts = session.beginTransaction();
Customer customer = session.load(Customer.class, 1L);
customer.setCust_level("VIP");
customer.setCust_linkman("李彦宏");
session.update(customer);
ts.commit();
session.close();
}
/**
* 4. 删除
*/
@Test
public void test04() {
Session session = HibernateUtils.openSession();
Transaction ts = session.beginTransaction();
Customer customer = session.load(Customer.class, 2L);
session.delete(customer);
ts.commit();
session.close();
}
}
HibernateUtils.java
package utils;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration;
public class HibernateUtils {
private static SessionFactory factory;
static {
Configuration config = new Configuration().configure();
factory = config.buildSessionFactory();
}
public static Session openSession() {
return factory.openSession();
}
public static Session getCurrentSession() {
return factory.getCurrentSession();
}
}
5.2 JavaBean规范
- 成员变量私有化,变成属性
- 属性:看的是
get/set方法